Reconstruction of a family house near Brno

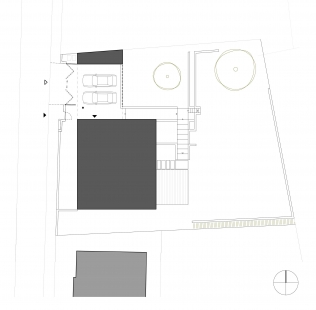
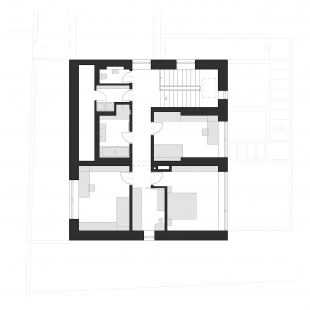
The existing house from the 1950s is located on the edge of the city in a quiet street consisting of similar standalone houses with predominantly pitched roofs. The plot is sloped with an elevation of 3.5 meters from the street level to the highest point of the garden at the eastern edge of the property. The basement of the house was originally used as technical space with a garage, featuring a room height of 2.15 meters. The first and second floors contained living rooms, sanitary facilities, and supplementary rooms. The remaining part in the attic was unused.
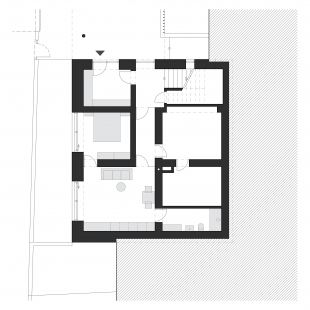
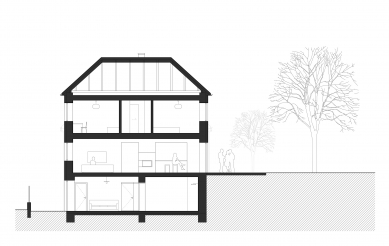
The initial plan for the building modifications was to "cleanse the house" of inconceivable extensions and create a more compact volume while simplifying its overall expression. The fundamental proposed building changes included the removal of the extension with the entrance staircase, lowering the basement floor by 0.5 meters for better usability as living spaces, and altering the shape of the roof. Load-bearing structures were preserved to the necessary extent, with openings created in the outer and inner load-bearing walls as well as internal partitions. The internal staircase, along with the ceiling in the adjacent hallway, was removed and replaced with a new, more comfortable staircase.
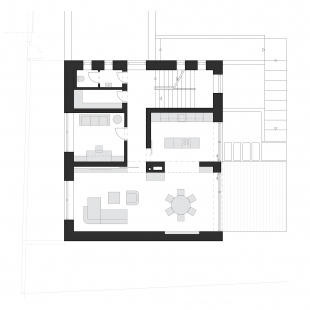
An integral part of the modifications to the house is the design of the entire plot. Both aspects are approached equally, with a strong emphasis on the mutual functioning of the internal layout and the garden. The most significant modifications in the garden behind the house include leveling the terrain to the floor level of the first floor. This allowed for a direct connection between the living floor and the garden, compared to the original state where entry to the garden was through the entrance hall, circumventing the house via the staircase.
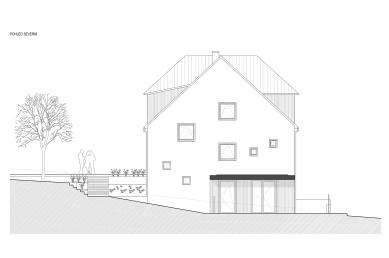
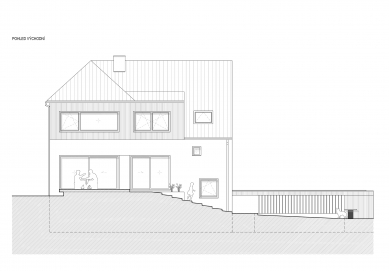
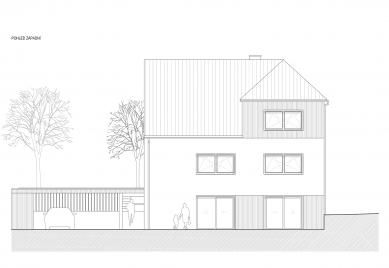
The façade solutions are based on a play with the composition of windows and work with basic materials. The choice of window size and placement reflects the functional use of interior spaces and combines two principles. Large glazing is proposed in the living rooms. Where possible, the interior is connected to the exterior through sliding doors – HS portals, while in other rooms, the windows feature a traditionally high sill.
In the utility rooms of the house and the staircase space, smaller square windows are chosen, distributed on the façade in an apparently random composition reflecting the movement along the staircase, simultaneously providing varied views from the interior.
The chosen façade materials combine rendered and wooden surfaces. The white render is complemented with vertical wooden cladding made of boards, located locally in front of the garden facing the street, at the entrance in conjunction with the wooden shelter, and in the part of the third floor, creating a separate mass that rises above the main roof of the house. The roof is made of sheet metal, standing seam, in a gray shade, as are other sheet metal elements. The frames of windows and entrance doors are wooden. The outdoor retaining walls and the base of the street fencing are made of exposed concrete, while the fencing itself is metal, alongside a wooden terrace; other paved areas are also made of concrete.
The initial plan for the building modifications was to "cleanse the house" of inconceivable extensions and create a more compact volume while simplifying its overall expression. The fundamental proposed building changes included the removal of the extension with the entrance staircase, lowering the basement floor by 0.5 meters for better usability as living spaces, and altering the shape of the roof. Load-bearing structures were preserved to the necessary extent, with openings created in the outer and inner load-bearing walls as well as internal partitions. The internal staircase, along with the ceiling in the adjacent hallway, was removed and replaced with a new, more comfortable staircase.
An integral part of the modifications to the house is the design of the entire plot. Both aspects are approached equally, with a strong emphasis on the mutual functioning of the internal layout and the garden. The most significant modifications in the garden behind the house include leveling the terrain to the floor level of the first floor. This allowed for a direct connection between the living floor and the garden, compared to the original state where entry to the garden was through the entrance hall, circumventing the house via the staircase.
The façade solutions are based on a play with the composition of windows and work with basic materials. The choice of window size and placement reflects the functional use of interior spaces and combines two principles. Large glazing is proposed in the living rooms. Where possible, the interior is connected to the exterior through sliding doors – HS portals, while in other rooms, the windows feature a traditionally high sill.
In the utility rooms of the house and the staircase space, smaller square windows are chosen, distributed on the façade in an apparently random composition reflecting the movement along the staircase, simultaneously providing varied views from the interior.
The chosen façade materials combine rendered and wooden surfaces. The white render is complemented with vertical wooden cladding made of boards, located locally in front of the garden facing the street, at the entrance in conjunction with the wooden shelter, and in the part of the third floor, creating a separate mass that rises above the main roof of the house. The roof is made of sheet metal, standing seam, in a gray shade, as are other sheet metal elements. The frames of windows and entrance doors are wooden. The outdoor retaining walls and the base of the street fencing are made of exposed concrete, while the fencing itself is metal, alongside a wooden terrace; other paved areas are also made of concrete.
The English translation is powered by AI tool. Switch to Czech to view the original text source.
0 comments
add comment