House with a bay window

The family house is situated on a gently sloping plot in a smaller mountain village. The basic mass shape of the house, with a rectangular floor plan covered by a gable roof, was determined by the local regulations of the municipality and the protected landscape area.
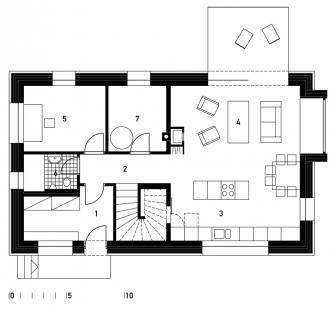
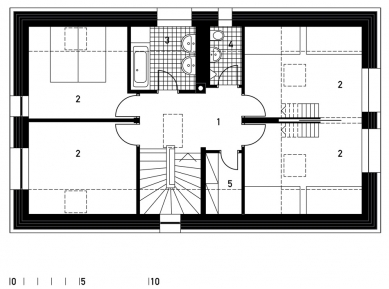
The internal layout of the house is simple and clear, based on the needs of its inhabitants. The social spaces, along with a study and a technical room, are on the ground floor, while the attic level is reserved for children's rooms and the parents' bedroom. The use of the maximum possible fifty-degree slope of the roof allowed for the creation of an additional floor in the attic. The "third" floor is partially used as an attic, and the remaining space enlarges the area of the children's rooms with inserted levels designated for sleeping or relaxation.
Structural Design
The building is founded on concrete strips using blocks for lost formwork. The exterior load-bearing walls as well as the interior partitions are constructed from 24 cm wide lime-sand bricks with increased insulation. For the partitions, bricks made from the same material, 11.5 cm wide, are used. The ceiling structure is made from hollow panels, allowing for spanning the entire width of the house without the need for supports.
The external masonry is insulated with 30 cm of mineral wool, placed in a system of vertical and horizontal battens that also support the wooden cladding of the facade. The facade is designed and executed as ventilated with horizontally laid wooden profiles of three different widths made from Siberian larch without surface treatment.
The roof is supported by a conventional truss with a peak rafter supported by a pair of columns. The above-standard insulation of the roof, at a thickness of 40 cm, necessitated the creation of a double rafter construction system. The roofing consists of folded strips of titanium zinc with a weathered finish. The eaves gutter is placed at the edge of the roof and facade slope. The vertical downpipes for rainwater drainage are concealed beneath the facade cladding.
Heating and Ventilation System
The main source for heating and water heating is electric energy. An integrated heat storage tank, heated by an electric coil, is located in the technical room. A set of five flat solar collectors and a fireplace stove with a water exchanger serves as a supplementary source. Heating for individual rooms is provided by radiators or convectors. The house is designed for controlled ventilation with heat recovery, featuring a unit located under the ceiling of the technical room.
The internal layout of the house is simple and clear, based on the needs of its inhabitants. The social spaces, along with a study and a technical room, are on the ground floor, while the attic level is reserved for children's rooms and the parents' bedroom. The use of the maximum possible fifty-degree slope of the roof allowed for the creation of an additional floor in the attic. The "third" floor is partially used as an attic, and the remaining space enlarges the area of the children's rooms with inserted levels designated for sleeping or relaxation.
Structural Design
The building is founded on concrete strips using blocks for lost formwork. The exterior load-bearing walls as well as the interior partitions are constructed from 24 cm wide lime-sand bricks with increased insulation. For the partitions, bricks made from the same material, 11.5 cm wide, are used. The ceiling structure is made from hollow panels, allowing for spanning the entire width of the house without the need for supports.
The external masonry is insulated with 30 cm of mineral wool, placed in a system of vertical and horizontal battens that also support the wooden cladding of the facade. The facade is designed and executed as ventilated with horizontally laid wooden profiles of three different widths made from Siberian larch without surface treatment.
The roof is supported by a conventional truss with a peak rafter supported by a pair of columns. The above-standard insulation of the roof, at a thickness of 40 cm, necessitated the creation of a double rafter construction system. The roofing consists of folded strips of titanium zinc with a weathered finish. The eaves gutter is placed at the edge of the roof and facade slope. The vertical downpipes for rainwater drainage are concealed beneath the facade cladding.
Heating and Ventilation System
The main source for heating and water heating is electric energy. An integrated heat storage tank, heated by an electric coil, is located in the technical room. A set of five flat solar collectors and a fireplace stove with a water exchanger serves as a supplementary source. Heating for individual rooms is provided by radiators or convectors. The house is designed for controlled ventilation with heat recovery, featuring a unit located under the ceiling of the technical room.
The English translation is powered by AI tool. Switch to Czech to view the original text source.
11 comments
add comment
Subject
Author
Date
jo, to by šlo
Tom
06.09.12 07:36
měřítko
blanch
06.09.12 09:16
Re: Tom
Martin
06.09.12 12:45
sníh, voda a led
šárka
06.09.12 04:12
Re: Tom +
Martin
06.09.12 08:44
show all comments