
The number of new passive houses in the Czech Republic increased by about a fifth last year
 |
"The figures provided are only indicative. Exact statistics still do not exist, so we draw from the frequency of interest from applicants for consultations during the project and construction at the Passive House Center, as well as from the data of the New Green Savings program, where the number of interested parties increased by nearly one hundred percent year-on-year last year," Vanický stated.
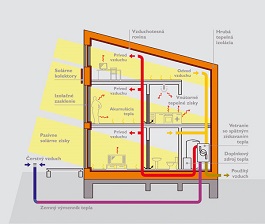
For a passive house, key is the recovery of heat, known as recuperation, where a system of pipes exchanges air while heat remains inside. The first house referred to as passive was built in 1990 in Darmstadt, Germany.
According to Vanický, the greatest interest in this type of construction is still among builders of family houses. There is also growing interest in apartment buildings, as exemplified by the development projects of the company JRD. "There is also great interest in the public sector. Last year, this specifically included primary and kindergartens, hospitals, municipal offices, children's and youth houses, as well as senior houses or cultural centers," Vanický added.
Last year, for instance, the Sýpka kindergarten was opened in Brno, a primary school in Psáry, the ZŠ Psáry kindergarten in the district of Prague-West, a kindergarten in Sedlejov in the Vysočina region, or a community house for seniors in Týnec nad Labem. "For a longer time, buildings of the University Center for Energy-Efficient Buildings in Buštěhrad and the Research and Innovation Center in Ostrava have been open and operationally verified," Vanický pointed out.
Examples of apartment buildings from recent years include the Ecocity Malešice project or Hyacint Modřany in Prague. The passive standard has also been applied to kindergartens in Moravské Budějovice or Semily, the Karel Malich School of Art in Holice, a primary school in Židlochovice, a senior house in Modřice in South Moravia, hospitals in Olomouc and Šternberk, or a public library in Rožnov pod Radhoštěm.
The English translation is powered by AI tool. Switch to Czech to view the original text source.
0 comments
add comment
Related articles
0
05.01.2023 | The share of passive houses in completed buildings is growing annually
1
16.03.2021 | The number of new passive houses in the Czech Republic grew by about one third last year
0
08.02.2019 | The share of new passive houses in the Czech Republic remained at six percent last year
0
08.02.2018 | The new director of the Passive House Center is Tomáš Vanický
0
09.02.2017 | The passive house of the year 2016 is a wooden building from Černošice
0
09.02.2017 | The share of new passive houses in the Czech Republic last year remained at 4.5%
0
04.07.2014 | A thousand young experts on passive houses are preparing to enter the market.
0
30.06.2014 | Passive houses do not have to be expensive at all, a study has shown
0
31.01.2014 | In Modřice, the first passive house for seniors has been opened for 64 million
0
13.11.2013 | The first certified passive apartment building in the Czech Republic is in Modřany
0
11.02.2013 | The number of passive houses in the Czech Republic is negligible; there are several hundred of them









